Bucket Sort
Example Problem
Given an array arr = [a1,a2,a3,a4,a5...,an] , we need to sort the array with the help of Bucket Sort algorithm.
Discussion
Bucket Sort is a sorting technique that sorts the elements by first dividing the elements into several groups called buckets. The elements inside each bucket are sorted using any of the suitable sorting algorithms or recursively calling the same algorithm.
Working of the Algorithm
Several buckets are created. Each bucket is filled with a specific range of elements. The elements inside the bucket are sorted using any other algorithm. Finally, the elements of the bucket are gathered to get the sorted array.
The process of bucket sort can be understood as a scatter-gather approach. The elements are first scattered into buckets then the elements of buckets are sorted. Finally, the elements are gathered in order.
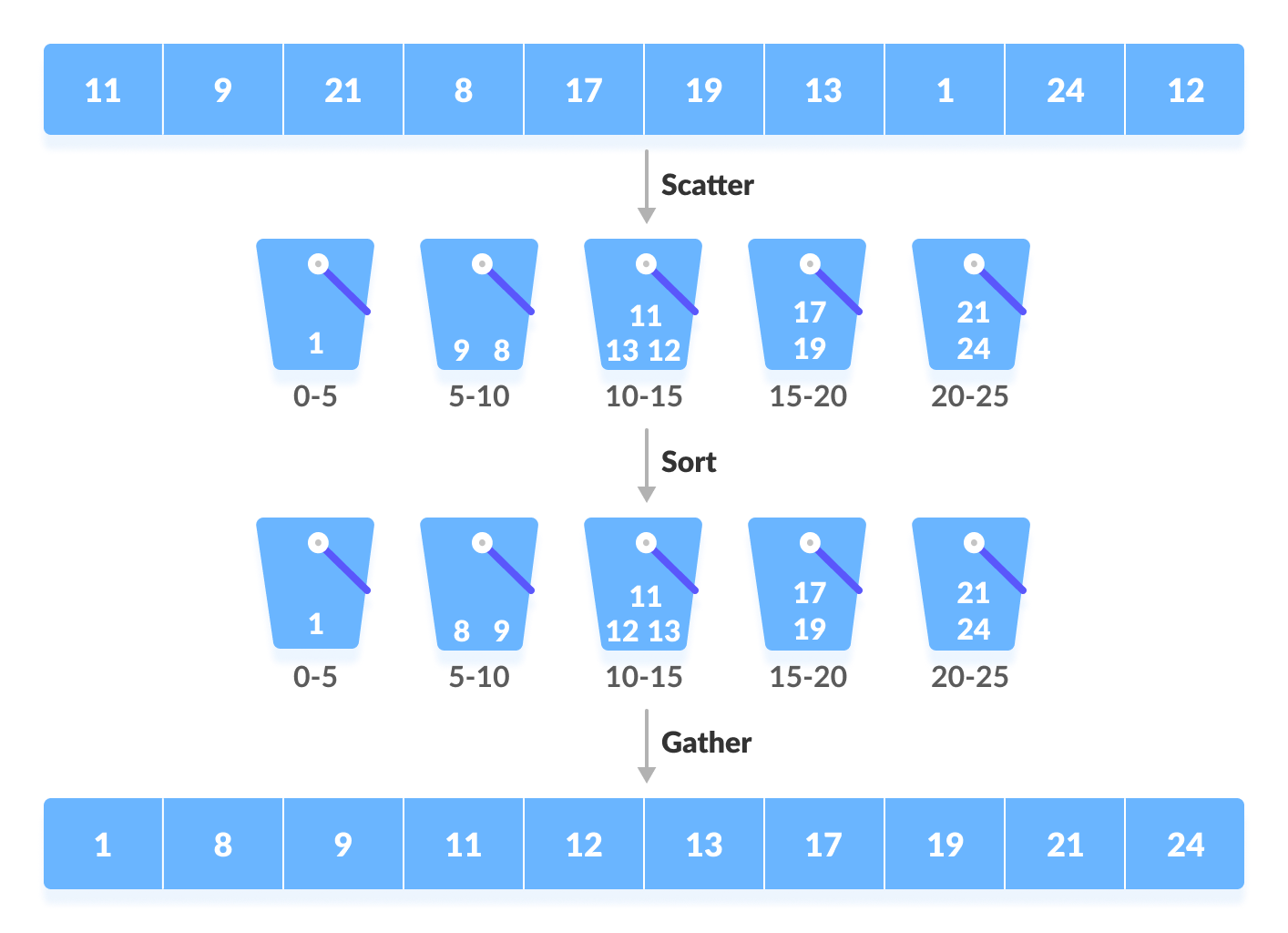
Illustration
Let's Sort an array of decimal numbers in th range 0 to 1.
Input array : 0.42 0.32 0.23 0.52 0.25 0.47 0.51
Create an array of size 10. Each slot of this array is used as a bucket for storing elements.
Insert elements into the buckets from the array. The elements are inserted according to the range of the bucket. And Sort them with a suitable sorting technique.
Representation of the buckets ->
| | | 0.23 | | 0.42 | 0.51 | | | | |
| 0 | 0 | 0.25 | 0.32 | 0.47 | 0.52 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Traverse From Left to right and put the elements back into array in the same order.
Sorted Array : 0.23 0.25 0.32 0.42 0.47 0.51 0.52
Code
Code For Bucket Sort.
void BucketSort(double a[],int n)
{
// creating vector array of size 10
vector <double> bucket[10];
// putting elements in respective bucket
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
bucket[ int(10 * a[i]) ].push_back(a[i]);
// sorting each bucket with quick sort
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
sort(bucket[i].begin(),bucket[i].end());
// picking from bucket and placing back to the array
for(int i=0, j=0;i<10;i++)
{
for(auto x : bucket[i])
{
a[j] = x;
j++;
}
}
// clearing the each bucket
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
bucket[i].clear();
}
Time Complexity
Worst Case Complexity : O ( n2 )
When there are elements of close range in the array, they are likely to be placed in the same bucket. This may result in some buckets having more number of elements than others. It makes the complexity depend on the sorting algorithm used to sort the elements of the bucket.
The complexity becomes even worse when the elements are in reverse order. If insertion sort is used to sort elements of the bucket, then the time complexity becomes O ( n2 ).
Best Case Complexity: O(n+k)
It occurs when the elements are uniformly distributed in the buckets with a nearly equal number of elements in each bucket. The complexity becomes even better if the elements inside the buckets are already sorted.
If insertion sort is used to sort elements of a bucket then the overall complexity in the best case will be linear ie. O(n+k). O(n) is the complexity for making the buckets and O(k) is the complexity for sorting the elements of the bucket using algorithms having linear time complexity at the best case.
Other Resources : GFG Blog