Lowest Common Ancestor
Given a rooted tree \(T\) of \(n\) nodes. The ancestors of a \(node\ u\) are all the nodes in the path from \(node\ u\) to \(root\) (excluding \(u\)).
Now Let's see how we can find \(LCA\) of two \(node\ u\) and \(v\).
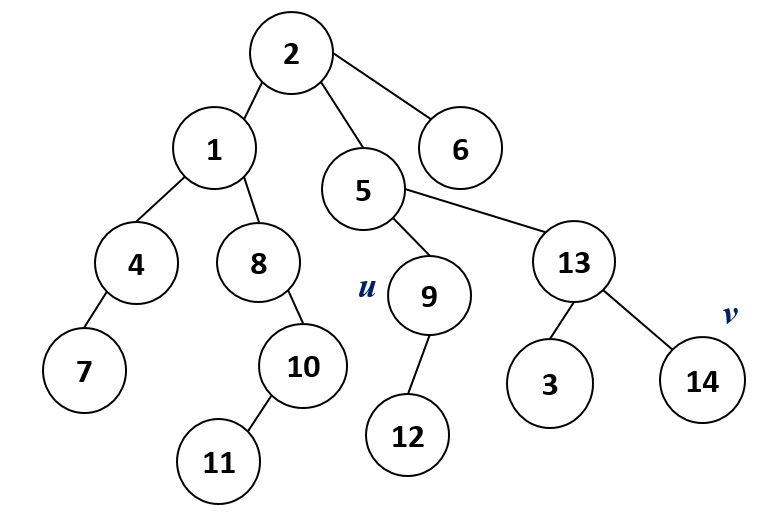
Algorithm \(1\) : \(O(n)\)
climb up from the deeper \(node\) such that \(depth[u] == depth[v]\).
Now climb up from both the node until \(u == v\).
Implementation :
int LCA(int u, int v){
if(depth[u] > depth[v])
swap(u, v);
int h = depth[v] - depth[u];
for(int i = 0; i < h; i++) // lifting v up to the same level as u
v = parent[v];
while(u != v){ // climbing up egde by egde from u and v
u = parent[u];
v = parent[v];
}
return u;
}
Here, as we are climbing edge by egde, hence in worst case it will take \(O(n)\) time to compute LCA.
Algorithm \(2\) : \(O(logn)\)
Instead of climbing edge by edge, we can make higher jumps from the node : say, from \(node\ u\) to \(2^i\) distant ancestor of \(u\). We need to precompute \(ancestor[n][k]\) : such that, \(ancestor[i][j]\) will store \(2^j\) distant ancestor of \(node\ i\).
\(n\) = no. of nodes if \(2^k > n\), then we jump off the tree. Hence \( k = 1 + log_2(n) \)
We know, \(2^j = 2^{j-1} + 2^{j-1}\) therefore, \(ancestor[i][j] = ancestor[\ ancestor[i][j-1]\ ][j-1]\) Note : \(parent[root] = -1\); \(ancestor[i][0]\) is simply the parent of \(node\ i\).
// Computing ancestor table
int k = 1 + log2(n);
vector<vector<int>> ancestor(n+1, vector<int> (k));
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ancestor[i][0] = parent[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(int j = 1; j < k; j++){
if(ancestor[i][j-1] != -1) // we didn't jump off the tree
ancestor[i][j] = ancestor[ ancestor[i][j-1] ][j-1]
else
ancestor[i][j] = -1
}
}
Binary Lifting :
Now say, we need to make a jump of height \(h = 45\) from a \(node\ u\).
\(h = 45 = (101101)_2 = (2^5 + 2^3 + 2^2 + 2^0) jumps\).
we can implement this jump as following :
int jump(int u, int h){
for(int i = 0; h && u != -1;i++){
if(h & 1)
u = ancestor[u][i];
h = h >> 1;
}
return u;
}
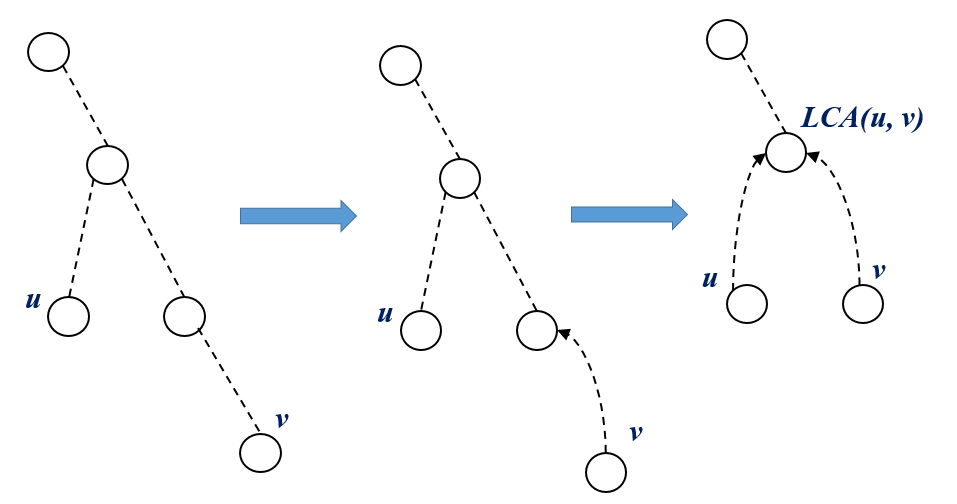
Computing LCA :
Using the \(Binary\ Lifting\) technique, make jump of a \(height = depth[v] - depth[u]\) from the deeper \(node\ v\).
if \(u == v\) already then \(return\ u\).
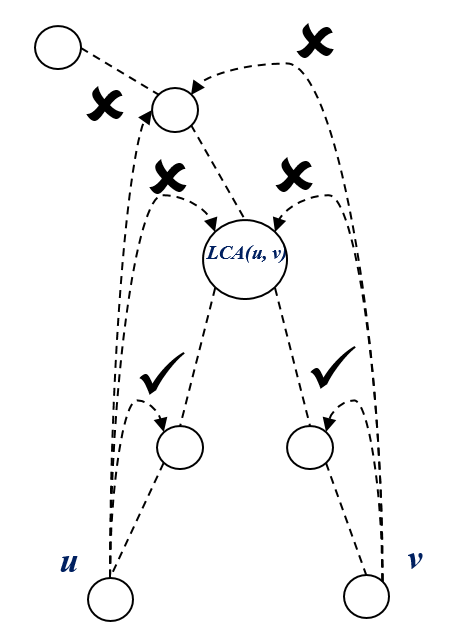
from \(node\ u\) and \(node\ v\), make jump as high as possible such that \(ancestor[u][jump]\ != ancestor[v][jump]\), then eventually we will reach a node, \(parent[u] = parent[v] = LCA(u, v)\)
thus \(return\ parent[u]\).
Implementation :
int LCA(int u, int v){
if(depth[u] > depth[v])
swap(u, v);
v = jump(v, depth[v] - depth[u]);
if(u == v)
return u;
int h = 1 + log2(depth[u]);
for(int i = h-1; i >= 0; i--){
if(ancestor[u][i] != -1 && ancestor[u][i] != ancestor[v][i]){
u = ancestor[u][i];
v = ancestor[v][i];
}
}
return parent[u];
}